A little history of reading: How the first books came to be
Published on: 03 December 2019 Author: Cerrie Burnell
Books and storytelling have long been part of our human identity. Author Cerrie Burnell shows this is why stories are for everyone – whatever your background.

We all know that glorious feeling of clutching a book in our hands. Whether it’s a brand-new gift, or something we’ve borrowed from a fabulous library, or perhaps a long-loved family treasure creased from re-reading...
But there is a specialness that comes from holding a story and knowing that you can step in or out of it, whenever you wish.
When my daughter asked me, ‘But how did the first book begin?’, I didn’t have a coherent answer. I’ve just always accepted that books are a kind of magic. But the journey of a book and how they first began is its very own cross-cultural, historical adventure that weaves its way around the globe.
Spoken word and cave drawings
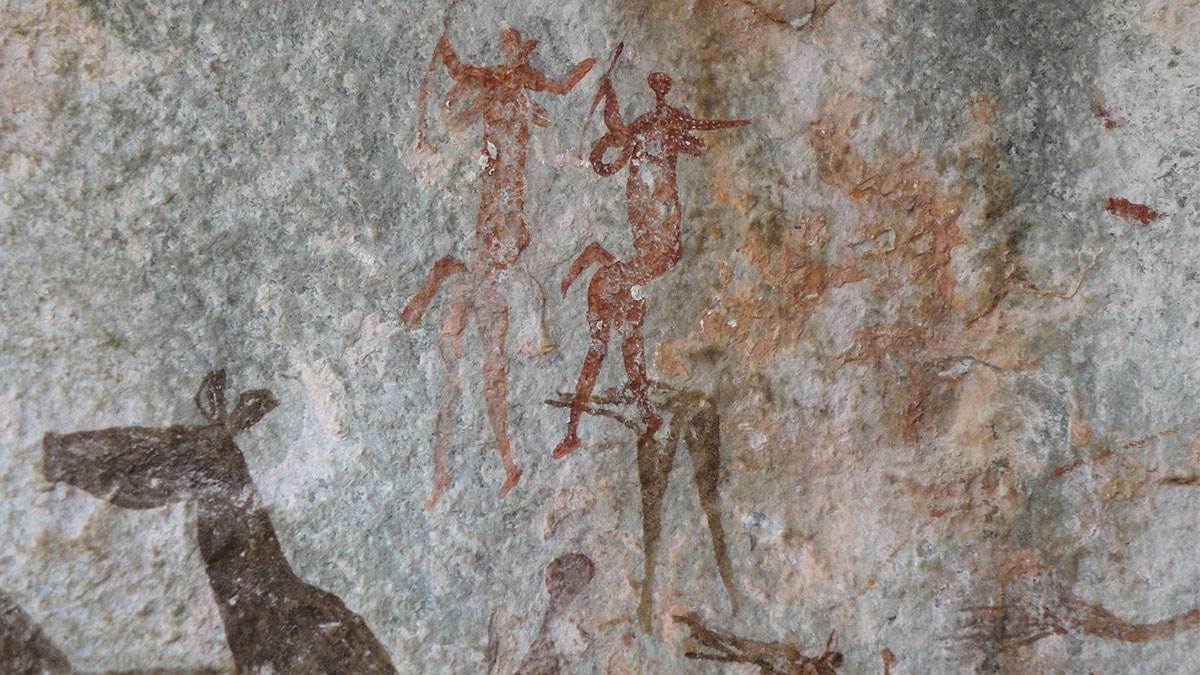
Before we had books, we had stories. Storytelling was a communal act: a retelling of daily life to teach a lesson, instil a warning or simply to entertain. Storytelling was a communal way of sharing joy and keeping the dark or danger at bay. This is how fairy tales began and how language and spoken word found its power.
Alongside storytelling, there are many examples of older civilisations recording their lives, through cave drawings or stone carvings. But the earliest examples of "writing" – either on stone slabs or impressed onto pieces of bark – were more to record numbers, lists, or convey information.
People needed to document their accounts, so in fact the very first written notes were more to convey maths than literature!
Scrolls and "pages"
The ancient Egyptians were the first society to use "pages", as such. They did this by weaving together stems of a papyrus plant, then flattening the woven stems by pounding them flat. This created a "page", which, when glued together, became a scroll.
This technique was used for hundreds of years and the Greeks and Romans soon adopted it. They would carefully wrap the scroll around a large piece of wood so it could be stored or transported and then unwound in a very grand gesture, to be read out loud. This method was used until the 8th century AD.
Slightly before this time, in another part of the world, parchment such as calf skin, or deer skin, began to be used as it was less likely to tear, and there was a shortage of papyrus. The parchment would be treated in alkaline then written over in ink.
The beginning of picture books
Around 600 AD, beautiful hand-sketched illustrations began appearing on parchment. These colourful, meticulously drawn pictures were called "illuminated manuscripts" and were wonderful to behold. They helped depict the story or enforce the importance of the message on the parchment. Really, this was the beginning of picture books.

The Greeks and Romans also invented wax tablets, which were blocks of wood layered with wax so you could scratch a message into them, then erase them and re-use them again and again (sort of like an etch-a-sketch!).
The first actual book written on paper is said to have been made in China. It was created using mulberries, hemp, bark and even fish to form a big pulp, that could be pressed and dried to form paper. Each sheet of paper was roughly the size of a newspaper and called a "leaf". As soon as the leaf was printed upon with ink by using wooden printing blocks, it was known as a "folio", which is another word for leaf.
The first ever books
Gradually, individual books, which were highly precious, were formed. Some of these books held highly important information or religious texts and others told glorious, wicked or wonderful stories. The first book ever written that we know of is The Epic of Gilgamesh: a mythical retelling of an important political figure from history.
In the 14th century, the Jikji was printed in Korea in movable (metal) type: a collection of Buddhist Zen teachings. A century later, in 1454, a German man called Johannes Gutenburg built a printing press to print the Gutenburg Bible, which led to printers springing up all across Europe.
Books could now be printed far more easily!
A man named Aldus Manutious founded a printing press in Venice with the desire to create pocket-sized books that retold the Greek Classics. His wish was for well-to-do folk to be able to pop the book into a satchel and carry it with them when cycling, meaning books could be transported everywhere.
Publishers and book clubs
In 1832, the first book covers appeared. In America and Britain, books which cost a penny were rewrites of gothic horror stories that soon earned themselves the nickname Penny Dreadful. However, not everyone could afford a penny per book, so groups of friends got together to split the cost and enjoy the dark, gory stories together: these were the first book clubs!
Also in the 19th century, aspiring publishers started printing hardback books aimed at wealthier households. There was a lot of snobbery around the difference in books: hardbacks were thought to be great works of fine literature, and paperbacks were thought to be less intelligent or silly.
Two American brothers named Boni set up a publishing company which sent books out by mail order. It went through some hard times but eventually triumphed and became Random House.

The Boni brothers were closely followed in 1935 by Penguin, a hugely successful British publisher that printed clearly branded books that appealed to everyone. This was only the start of the publishing world as we know it and it blossomed even further with the invention of mainstream computers, books on tape or CD (which we now know as audiobooks) and the ebook or Kindle.
People are reading and accessing stories in many different formats with companies shipping to the seven corners of the world.
All stories are equal
Books are a global phenomenon and, like stories, they belong to everyone. No singular set of characters, nor type of story, has any authority over another. Just like all cultures and histories, all stories have a place upon the bookcases of the libraries of the world.
For me, holding a physical book in my hand, whether it’s a hardback or a paperback, is a kind of enchantment. (Though I do also love an audiobook to listen to last thing at night.) If you can’t find a book that reflects your experience of the world, then just maybe you need to write that book.
Learning about different communities, and seeing ourselves represented in the pages of epic tales, is magic for the soul – it teaches us resilience and compassion and many things beyond...
More little history: Learn about the libraries and why they matter
More about BookTrust Writers in Residence
Note: This article was amended on 21 September 2021.
Topics: Historical, Writer in Residence, Writing, Features, Cerrie Burnell






Add a comment